[ 1950s ]
[ 1960s ]
[ 1970s ]
[ 1980s ]
[ 1990s ]
[ 2000s ]
[ Growth ]
[ FAQ ]
[ Sources ]
Hobbes' Internet Timeline v5.6
by
Robert H'obbes' Zakon
Internet Evangelist
Hobbes' Internet Timeline Copyright (c)1993-2002 by Robert H Zakon.
Permission is granted for use of this document in whole or in part for
non-commercial purposes as long as this Copyright notice and a link to
this document, at the archive listed at the end, is included.
A copy of the material the Timeline appears in is requested.
For commercial uses, please contact the author first.
Links to this document are welcome after e-mailing the author with the
document URL where the link will appear. As the Timeline is frequently
updated, copies to other locations on the Internet are not permitted.
If you enjoy the Timeline or make use of it in some way, please
consider a contribution.
- 1957
- USSR launches Sputnik, first artificial earth satellite. In response,
US forms the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA),
the following year, within the Department of Defense (DoD) to
establish US lead in science and technology applicable to the
military (:amk:)
- 1961
- Leonard Kleinrock, MIT: "Information Flow in Large Communication Nets" (May 31)
- First paper on packet-switching (PS) theory
- 1962
- J.C.R. Licklider & W. Clark, MIT: "On-Line Man Computer Communication" (August)
- Galactic Network concept encompassing distributed social interactions
- 1964
- Paul Baran, RAND: "On Distributed Communications Networks"
- Packet-switching networks; no single outage point
- 1965
- ARPA sponsors study on "cooperative network of time-sharing
computers"
- TX-2 at MIT Lincoln Lab and AN/FSQ-32 at System Development Corporation
(Santa Monica, CA) are directly linked (without packet switches) via
a dedicated 1200bps phone line; Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)
computer at ARPA later added to form "The Experimental Network"
- 1966
- Lawrence G. Roberts, MIT: "Towards a Cooperative Network of Time-Shared
Computers" (October)
- 1967
- ARPANET design discussions held by Larry Roberts at ARPA IPTO PI
meeting in Ann Arbor, Michigan (April)
- ACM Symposium on Operating System Principles in Gatlinburg, Tennessee (October)
- First design paper on ARPANET published by Larry Roberts:
"Multiple Computer Networks and Intercomputer Communication
- First meeting of the three independent packet network teams
(RAND, NPL, ARPA)
- National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in Middlesex, England develops NPL
Data Network under Donald Watts Davies who coins the term packet.
The NPL network, an experiment in packet-switching, used 768kbps
lines
- 1968
- PS-network presented to the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
- Request for proposals for ARPANET sent out in August; responses received
in September
- University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) awarded Network Measurement
Center contract in October
- Bolt Beranek and Newman, Inc. (BBN) awarded Packet Switch contract
to build Interface Message Processors (IMPs)
- US Senator Edward Kennedy sends a congratulatory telegram to BBN for
its million-dollar ARPA contract to build the "Interfaith"
Message Processor, and thanking them for their ecumenical efforts
- Network Working Group (NWG), headed by Steve Crocker, loosely organized to
develop host level protocols for communication over the ARPANET. (:vgc:)
- Tymnet built as part of Tymshare service (:vgc:)
- 1969
- ARPANET commissioned by DoD for research into networking
- Nodes are stood up as BBN builds each IMP [Honeywell DDP-516 mini
computer with 12K of memory]; AT&T provides 50kbps lines
- Node 1: UCLA (30 August, hooked up 2 September)
- Node 2: Stanford Research Institute (SRI) (1 October)
- Network Information Center (NIC)
- SDS940/Genie
- Doug Engelbart's project on "Augmentation of Human Intellect"
- Node 3: University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB) (1 November)
- Culler-Fried Interactive Mathematics
- IBM 360/75, OS/MVT
- Node 4: University of Utah (December)
- Graphics
- DEC PDP-10, Tenex
- Diagram of the 4-node ARPAnet
- First Request for Comment (RFC): "Host Software" by Steve Crocker (7 April)
- RFC 4: Network Timetable
- First packets sent by Charley Kline at UCLA as he tried logging
into SRI. The first attempt resulted in the system crashing
as the letter G of LOGIN was entered. (October 29) [ Log entry ]
- Univ of Michigan, Michigan State and Wayne State Univ establish X.25-based
Merit network for students, faculty, alumni (:sw1:)
- 1970
- First publication of the original ARPANET Host-Host protocol:
C.S. Carr, S. Crocker, V.G. Cerf, "HOST-HOST Communication
Protocol in the ARPA Network," in AFIPS Proceedings of SJCC
(:vgc:)
- First report on ARPANET at AFIPS: "Computer Network Development
to Achieve Resource Sharing" (March)
- ALOHAnet, the first packet radio network, developed by Norman
Abramson, Univ of Hawaii, becomes operational (July) (:sk2:)
- connected to the ARPANET in 1972
- ARPANET hosts start using Network Control Protocol (NCP),
first host-to-host protocol
- First cross-country link installed by AT&T between UCLA and BBN
at 56kbps. This line is later replaced by another between
BBN and RAND. A second line is added between MIT and Utah
- 1971
- 15 nodes (23 hosts): UCLA, SRI, UCSB, Univ of Utah, BBN, MIT, RAND, SDC,
Harvard, Lincoln Lab, Stanford, UIU(C), CWRU, CMU, NASA/Ames
- BBN starts building IMPs using the cheaper Honeywell 316. IMPs
however are limited to 4 host connections, and so BBN develops
a terminal IMP (TIP) that supports up to 64 terminals (September)
- Ray Tomlinson of BBN invents email program to send messages across a
distributed network. The original program was derived from two others:
an intra-machine email program (SENDMSG) and an experimental file
transfer program (CPYNET) (:amk:irh:)
- 1972
- Ray Tomlinson (BBN) modifies email program for ARPANET where it
becomes a quick hit. The @ sign was chosen from the punctuation
keys on Tomlinson's Model 33 Teletype for its "at" meaning
(March)
- Larry Roberts writes first email management program (RD) to list,
selectively read, file, forward, and respond to messages (July)
- International Conference on Computer Communications (ICCC) at
the Washington D.C. Hilton with demonstration of ARPANET
between 40 machines and the Terminal Interface Processor (TIP)
organized by Bob Kahn. (October)
- First computer-to-computer chat takes place at UCLA, and is repeated
during ICCC, as psychotic PARRY (at Stanford) discusses its problems
with the Doctor (at BBN).
- International Network Working Group (INWG) formed in October as a result
of a meeting at ICCC identifying the need for a combined effort in
advancing networking technologies. Vint Cerf appointed first Chair.
By 1974, INWG became IFIP WG 6.1 (:vgc:)
- Louis Pouzin leads the French effort to build its own ARPANET
- CYCLADES
- RFC 318: Telnet specification
- 1973
- First international connections to the ARPANET: University College of
London (England) via NORSAR (Norway)
- Bob Metcalfe's Harvard PhD Thesis outlines idea for Ethernet. The concept was tested on Xerox
PARC's Alto computers, and the first Ethernet network called
the Alto Aloha System (May) (:amk:)
- Bob Kahn poses Internet problem, starts internetting research program
at ARPA. Vinton Cerf sketches gateway architecture in March on back
of envelope in a San Francisco hotel lobby (:vgc:)
- Cerf and Kahn present basic Internet ideas at INWG in September at Univ of
Sussex, Brighton, UK (:vgc:)
- RFC 454: File Transfer specification
- Network Voice Protocol (NVP) specification (RFC 741) and implementation enabling
conference calls over ARPAnet. (:bb1:)
- SRI (NIC) begins publishing ARPANET News in March; number of ARPANET users
estimated at 2,000
- ARPA study shows email composing 75% of all ARPANET traffic
- Christmas Day Lockup - Harvard IMP hardware problem leads it to broadcast
zero-length hops to any ARPANET destination, causing all other IMPs to
send their traffic to Harvard (25 December)
- RFC 527: ARPAWOCKY
- RFC 602: The Stockings Were Hung by the Chimney with Care
- 1974
- Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn publish "A Protocol for Packet Network
Interconnection" which specified in detail the design of a
Transmission Control Program (TCP). [IEEE Trans Comm] (:amk:)
- BBN opens Telenet, the first public packet data service (a commercial
version of ARPANET) (:sk2:)
- 1975
- Operational management of Internet transferred to DCA (now DISA)
- First ARPANET mailing list, MsgGroup, is created by Steve Walker.
Einar Stefferud soon took over as moderator as the list was not
automated at first. A science fiction list, SF-Lovers, was to
become the most popular unofficial list in the early days
- John Vittal develops MSG, the first all-inclusive email program
providing replying, forwarding, and filing capabilities.
- Satellite links cross two oceans (to Hawaii and UK) as the first TCP
tests are run over them by Stanford, BBN, and UCL
- "Jargon File", by Raphael Finkel at SAIL, first released (:esr:)
- Shockwave Rider by John Brunner (:pds:)
- 1976
- Elizabeth II, Queen of the United Kingdom sends out an email
on 26 March from the Royal Signals and Radar Establishment (RSRE)
in Malvern
- UUCP (Unix-to-Unix CoPy) developed at AT&T Bell Labs and distributed
with UNIX one
year later.
- Multiprocessing Pluribus IMPs are deployed
- 1977
- THEORYNET created by Larry Landweber at Univ of Wisconsin providing
electronic mail to over 100 researchers in computer science
(using a locally developed email system over TELENET)
- RFC 733: Mail specification
- Tymshare spins out Tymnet under pressure from TELENET. Both go on to
develop X.25 protocol standard for virtual circuit style packet
switching (:vgc:)
- First demonstration of ARPANET/SF Bay Packet Radio Net/Atlantic SATNET
operation of Internet protocols with BBN-supplied gateways in July (:vgc:)
- 1978
- TCP split into TCP and IP (March)
- RFC 748: TELNET RANDOMLY-LOSE Option
- 1979
- Meeting between Univ of Wisconsin, DARPA, National Science Foundation
(NSF), and computer scientists from many universities to establish a Computer
Science Department research computer network (organized by Larry Landweber).
- USENET established using UUCP between Duke and UNC by Tom Truscott,
Jim Ellis, and Steve Bellovin. All original groups were under
net.* hierarchy.
- First MUD, MUD1, by Richard Bartle and Roy Trubshaw at U of Essex
- ARPA establishes the Internet Configuration Control Board (ICCB)
- Packet Radio Network (PRNET) experiment starts with DARPA funding.
Most communications take place between mobile vans. ARPANET
connection via SRI.
- On April 12, Kevin MacKenzie emails the MsgGroup a suggestion of adding
some emotion back into the dry text medium of email, such as -) for
indicating a sentence was tongue-in-cheek. Though flamed by many at
the time, emoticons became widely used
- 1980
- ARPANET grinds to a complete halt on 27 October because of an
accidentally-propagated status-message virus
- First C/30-based IMP at BBN
- 1981
- BITNET, the "Because It's Time NETwork"
- Started as a cooperative network at the City University of New York,
with the first connection to Yale (:feg:)
- Original acronym stood for 'There' instead of 'Time' in reference to
the free NJE protocols provided with the IBM systems
- Provides electronic mail and listserv servers to distribute
information, as well as file transfers
- CSNET (Computer Science NETwork) built by a collaboration of
computer scientists and Univ of Delaware, Purdue Univ, Univ of Wisconsin,
RAND Corporation and BBN through seed money granted by NSF to
provide networking services (especially email) to university
scientists with no access to ARPANET. CSNET later becomes known
as the Computer and Science Network. (:amk,lhl:)
- C/30 IMPs predominate the network; first C/30 TIP at SAC
- Minitel (Teletel) is deployed across France by France Telecom.
- True Names by Vernor Vinge (:pds:)
- RFC 801: NCP/TCP Transition Plan
- 1982
- Norway leaves network to become an Internet connection via TCP/IP
over SATNET; UCL does the same
- DCA and ARPA establish the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and
Internet Protocol (IP), as the protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP,
for ARPANET. (:vgc:)
- This leads to one of the first definitions of an "internet"
as a connected set of networks, specifically those using TCP/IP,
and "Internet" as connected TCP/IP internets.
- DoD declares TCP/IP suite to be standard for DoD (:vgc:)
- EUnet (European UNIX Network) is created by EUUG to provide email and
USENET services. (:glg:)
- original connections between the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden, and UK
- Exterior Gateway Protocol (RFC 827) specification. EGP is used for
gateways between networks.
- 1983
- Name server developed at Univ of Wisconsin, no longer requiring users
to know the exact path to other systems
- Cutover from NCP to TCP/IP (1 January)
- No more Honeywell or Pluribus IMPs; TIPs replaced by TACs (terminal
access controller)
- Stuttgart and Korea get connected
- Movement Information Net (MINET) started early in the year in
Europe, connected to Internet in Sept
- CSNET / ARPANET gateway put in place
- ARPANET split into ARPANET and MILNET; the latter became integrated
with the Defense Data Network created the previous year. 68 of the
113 existing nodes went to MILNET
- Desktop workstations come into being, many with Berkeley UNIX (4.2 BSD)
which includes IP networking software (:mpc:)
- Networking needs switch from having a single, large time sharing computer
connected to the Internet at each site, to instead connecting entire local
networks
- Internet Activities Board (IAB) established, replacing ICCB
- EARN (European Academic and Research Network) established. Very
similar to the way BITNET works with a gateway funded by IBM
- FidoNet developed by Tom Jennings
- 1984
- Domain Name System (DNS) introduced
- Number of hosts breaks 1,000
- JUNET (Japan Unix Network) established using UUCP
- JANET (Joint Academic Network) established in the UK using the
Coloured Book protocols; previously SERCnet
- Moderated newsgroups introduced on USENET (mod.*)
- Neuromancer by William Gibson
- Canada begins a one-year effort to network its universities.
The NetNorth Network is connected to BITNET in Ithaca from Toronto (:kf1:)
- Kremvax message announcing USSR connectivity to USENET
- 1985
- Whole Earth 'Lectronic Link (WELL) started
- Information Sciences Institute (ISI) at USC is given responsibility for DNS root
management by DCA, and SRI for DNS NIC registrations
- Symbolics.com is assigned on 15 March to become the first registered domain.
Other firsts: cmu.edu, purdue.edu, rice.edu, berkeley.edu, ucla.edu,
rutgers.edu, bbn.com (24 Apr); mit.edu (23 May); think.com (24 may);
css.gov (June); mitre.org, .uk (July)
- 100 years to the day of the last spike being driven on the cross-Canada
railroad, the last Canadian university is connected to NetNorth in a one
year effort to have coast-to-coast connectivity. (:kf1:)
- RFC 968: 'Twas the Night Before Start-up
- 1986
- NSFNET created (backbone speed of 56Kbps)
- NSF establishes 5 super-computing centers to provide high-computing
power for all (JVNC@Princeton, PSC@Pittsburgh, SDSC@UCSD, NCSA@UIUC,
Theory Center@Cornell).
- This allows an explosion of connections, especially from
universities.
- NSF-funded SDSCNET, JVNCNET, SURANET, and NYSERNET operational (:sw1:)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and Internet Research Task
Force (IRTF) comes into existence under the IAB. First IETF meeting held in January
at Linkabit in San Diego
- The first Freenet (Cleveland) comes on-line 16 July under the auspices
of the Society for Public Access Computing (SoPAC). Later Freenet program
management assumed by the National Public Telecomputing Network (NPTN)
in 1989 (:sk2,rab:)
- Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) designed to enhance Usenet news
performance over TCP/IP.
- Mail Exchanger (MX) records developed by Craig Partridge allow
non-IP network hosts to have domain addresses.
- The great USENET name change; moderated newsgroups changed in 1987.
- BARRNET (Bay Area Regional Research Network) established using high
speed links. Operational in 1987.
- New England gets cut off from the Net as AT&T suffers a fiber optics
cable break between Newark/NJ and White Plains/NY. Yes, all seven
New England ARPANET trunk lines were in the one severed cable.
Outage took place between 1:11 and 12:11 EST on 12 December
- 1987
- NSF signs a cooperative agreement to manage the NSFNET backbone with
Merit Network, Inc. (IBM and MCI involvement was through an agreement
with Merit). Merit, IBM, and MCI later founded ANS.
- UUNET is founded with Usenix funds to provide commercial UUCP and
Usenet access. Originally an experiment by Rick Adams and Mike O'Dell
- First TCP/IP Interoperability Conference (March), name changed in 1988
to INTEROP
- Email link established between Germany and China using CSNET protocols, with
the first message from China sent on 20 September. (:wz1:)
- The concept and plan for a national US research and education network is
proposed by Gordon Bell et al in a report to the Office of Science and
Technology, written in response to a congressional request by Al Gore.
(Nov) It would take four years until the establishment of this network
by Congress (:gb1:)
- 1000th RFC: "Request For Comments reference guide"
- Number of hosts breaks 10,000
- Number of BITNET hosts breaks 1,000
- 1988
- 2 November - Internet worm burrows through the Net, affecting ~6,000
of the 60,000 hosts on the Internet (:ph1:)
- CERT (Computer Emergency Response Team) formed by DARPA in response to
the needs exhibited during the Morris worm incident. The worm is
the only advisory issued this year.
- DoD chooses to adopt OSI and sees use of TCP/IP as an interim. US
Government OSI Profile (GOSIP) defines the set of protocols to be
supported by Government purchased products (:gck:)
- Los Nettos network created with no federal funding, instead supported
by regional members (founding: Caltech, TIS, UCLA, USC, ISI).
- NSFNET backbone upgraded to T1 (1.544Mbps)
- CERFnet (California Education and Research Federation network) founded
by Susan Estrada.
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) established in December
with Jon Postel as its Director. Postel was also the RFC Editor
and US Domain registrar for many years.
- Internet Relay Chat (IRC) developed by Jarkko Oikarinen (:zby:)
- First Canadian regionals join NSFNET: ONet via Cornell, RISQ via
Princeton, BCnet via Univ of Washington (:ec1:)
- FidoNet gets connected to the Net, enabling the exchange of email
and news (:tp1:)
- The first multicast tunnel is established between Stanford and BBN
in the Summer of 1988.
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Canada (CA), Denmark (DK), Finland (FI), France (FR),
Iceland (IS), Norway (NO), Sweden (SE)
- 1989
- Number of hosts breaks 100,000
- RIPE (Reseaux IP Europeens) formed (by European service providers) to
ensure the necessary administrative and technical coordination to
allow the operation of the pan-European IP Network. (:glg:)
- First relays between a commercial electronic mail carrier and the
Internet: MCI Mail through the Corporation for the National Research
Initiative (CNRI), and CompuServe through Ohio State Univ (:jg1,ph1:)
- Corporation for Research and Education Networking (CREN) is formed
by merging CSNET into BITNET (August)
- AARNET - Australian Academic Research Network - set up by AVCC and
CSIRO; introduced into service the following year (:gmc:)
- First link between Australia and NSFNET via Hawaii on 23 June
- Cuckoo's Egg by Clifford Stoll tells the real-life tale of a
German cracker group who infiltrated numerous US facilities
- UCLA sponsors the Act One symposium to celebrate ARPANET's 20th anniversary and
its decommissioning (August)
- RFC 1121: Act One - The Poems
- RFC 1097: TELNET SUBLIMINAL-MESSAGE Option
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Australia (AU), Germany (DE), Israel (IL),
Italy (IT), Japan (JP), Mexico (MX), Netherlands (NL), New Zealand (NZ),
Puerto Rico (PR), United Kingdom (UK)
- 1990
- ARPANET ceases to exist
- Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is founded by Mitch Kapor
- Archie released by Peter Deutsch, Alan Emtage, and Bill Heelan at McGill
- Hytelnet released by Peter Scott (Univ of Saskatchewan)
- The World comes on-line (world.std.com), becoming the first commercial
provider of Internet dial-up access
- ISO Development Environment (ISODE) developed to provide an approach for
OSI migration for the DoD. ISODE software allows OSI application to
operate over TCP/IP (:gck:)
- CA*net formed by 10 regional networks as national Canadian backbone
with direct connection to NSFNET (:ec1:)
- The first remotely operated machine to be hooked up to the Internet, the
Internet Toaster by John Romkey, (controlled via SNMP) makes its debut at
Interop.
- RFC 1149: A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams on Avian Carriers.
Implementation is completed 11 years later by the Bergen Linux Users Group (28 Apr 2001)
- RFC 1178: Choosing a Name for Your Computer
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Argentina (AR), Austria (AT), Belgium (BE),
Brazil (BR), Chile (CL), Greece (GR), India (IN), Ireland (IE), Korea (KR),
Spain (ES), Switzerland (CH)
- 1991
- First connection takes place between Brazil, by Fapesp, and the Internet
at 9600 baud.
- Commercial Internet eXchange (CIX) Association, Inc. formed by General
Atomics (CERFnet), Performance Systems International, Inc. (PSInet),
and UUNET Technologies, Inc. (AlterNet), after NSF lifts restrictions
on the commercial use of the Net (March) (:glg:)
- Wide Area Information Servers (WAIS), invented by Brewster Kahle,
released by Thinking Machines Corporation
- Gopher released by Paul Lindner and Mark P. McCahill from
the Univ of Minnesota
- World-Wide Web (WWW) released by CERN; Tim Berners-Lee developer (:pb1:)
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) released by Philip Zimmerman (:ad1:)
- US High Performance Computing Act (Gore 1) establishes the National
Research and Education Network (NREN)
- NSFNET backbone upgraded to T3 (44.736Mbps)
- NSFNET traffic passes 1 trillion bytes/month and 10 billion packets/month
- Defense Data Network NIC contract awarded by DISA to Government Systems Inc.
who takes over from SRI in May
- Start of JANET IP Service (JIPS) which signaled the changeover from
Coloured Book software to TCP/IP within the UK academic network.
IP was initially 'tunneled' within X.25. (:gst:)
- RFC 1216: Gigabit Network Economics and Paradigm Shifts
- RFC 1217: Memo from the Consortium for Slow Commotion Research (CSCR)
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Croatia (HR), Czech Republic (CZ), Hong Kong (HK),
Hungary (HU), Poland (PL), Portugal (PT), Singapore (SG), South Africa (ZA),
Taiwan (TW), Tunisia (TN)
- 1992
- Internet Society (ISOC) is chartered (January)
- IAB reconstituted as the Internet Architecture Board and becomes
part of the Internet Society
- Number of hosts breaks 1,000,000
- First MBONE audio multicast (March) and video multicast (November)
- RIPE Network Coordination Center (NCC) created in April to provide
address registration and coordination services to the European
Internet community (:dk1:)
- Veronica, a gopherspace search tool, is released by Univ of Nevada
- World Bank comes on-line
- The term "surfing the Internet" is coined by Jean Armour Polly (:jap:)
- Zen and the Art of the Internet is published
by Brendan Kehoe (:jap:)
- Internet Hunt started by Rick Gates
- RFC 1300: Remembrances of Things Past
- RFC 1313: Today's Programming for KRFC AM 1313 - Internet Talk Radio
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Antarctica (AQ), Cameroon (CM), Cyprus (CY),
Ecuador (EC), Estonia (EE), Kuwait (KW), Latvia (LV), Luxembourg (LU),
Malaysia (MY), Slovakia (SK), Slovenia (SI), Thailand (TH), Venezuela (VE)
- 1993
- InterNIC created by NSF to provide specific Internet services: (:sc1:)
- directory and database services (AT&T)
- registration services (Network Solutions Inc.)
- information services (General Atomics/CERFnet)
- US White House comes on-line (http://www.whitehouse.gov/):
- President Bill Clinton: president@whitehouse.gov
- Vice-President Al Gore: vice-president@whitehouse.gov
- Worms of a new kind find their way around the Net - WWW Worms (W4),
joined by Spiders, Wanderers, Crawlers, and Snakes ...
- Internet Talk Radio begins broadcasting (:sk2:)
- United Nations (UN) comes on-line (:vgc:)
- US National Information Infrastructure Act
- Businesses and media begin taking notice of the Internet
- InterCon International KK (IIKK) provides Japan's first commercial
Internet connection in September. TWICS, though an IIKK leased
line, begins offering dial-up accounts the following month (:tb1:)
- Mosaic takes the Internet by storm; WWW proliferates at a 341,634%
annual growth rate of service traffic. Gopher's growth is 997%.
- RFC 1437: The Extension of MIME Content-Types to a New Medium
- RFC 1438: IETF Statements of Boredom (SOBs)
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Bulgaria (BG), Costa Rica (CR), Egypt (EG),
Fiji (FJ), Ghana (GH), Guam (GU), Indonesia (ID), Kazakhstan (KZ), Kenya
(KE), Liechtenstein (LI), Peru (PE), Romania (RO), Russian Federation
(RU), Turkey (TR), Ukraine (UA), UAE (AE), US Virgin Islands (VI)
- 1994
- ARPANET/Internet celebrates 25th anniversary
- Communities begin to be wired up directly to the Internet
(Lexington and Cambridge, Mass., USA)
- US Senate and House provide information
servers
- Shopping malls arrive on the Internet
- First cyberstation, RT-FM, broadcasts from Interop in Las Vegas
- The National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) suggests that
GOSIP should incorporate TCP/IP and drop the "OSI-only" requirement
(:gck:)
- Arizona law firm of Canter & Siegel "spams" the Internet with email
advertising green card lottery services; Net citizens flame back
- NSFNET traffic passes 10 trillion bytes/month
- Yes, it's true - you can now order pizza from the Hut online
- WWW edges out telnet to become 2nd most popular service on the Net
(behind ftp-data) based on % of packets and bytes traffic distribution
on NSFNET
- Japanese Prime Minister on-line (http://www.kantei.go.jp/)
- UK's HM Treasury on-line (http://www.hm-treasury.gov.uk/)
- New Zealand's Info Tech Prime Minister on-line
(http://www.govt.nz/)
- First Virtual, the first cyberbank, open up for business
- Radio stations start rockin' (rebroadcasting) round the clock on the Net:
WXYC at Univ of NC, KJHK at Univ of KS-Lawrence, KUGS at Western WA Univ
- IPng recommended by IETF at its Toronto meeting (July) and approved by IESG
in November. Later documented as RFC 1752
- The first banner ads appear on hotwired.com in October. They were for Zima
(a beverage) and AT&T
- Trans-European Research and Education Network Association (TERENA) is
formed by the merger of RARE and EARN, with representatives from 38
countries as well as CERN and ECMWF. TERENA's aim is to "promote
and participate in the development of a high quality international
information and telecommunications infrastructure for the benefit
of research and education" (October)
- After noticing that many network software vendors used domain.com in their
documentation examples, Bill Woodcock and Jon Postel register the domain.
Sure enough, after looking at the domain access logs, it was evident that
many users were using the example domain in configuring their applications.
- RFC 1605: SONET to Sonnet Translation
- RFC 1606: A Historical Perspective On The Usage Of IP Version 9
- RFC 1607: A VIEW FROM THE 21ST CENTURY
- Countries connecting to NSFNET: Algeria (DZ), Armenia (AM), Bermuda (BM), Burkina
Faso (BF), China (CN), Colombia (CO), Jamaica (JM), Jordan (JO), Lebanon (LB),
Lithuania (LT), Macao (MO), Morocco (MA), New Caledonia (NC), Nicaragua (NI),
Niger (NE), Panama (PA), Philippines (PH), Senegal (SN), Sri Lanka (LK),
Swaziland (SZ), Uruguay (UY), Uzbekistan (UZ)
- Top 10 Domains by Host #: com, edu, uk, gov, de, ca, mil, au, org, net
- 1995
- NSFNET reverts back to a research network. Main US backbone traffic now
routed through interconnected network providers
- The new NSFNET is born as NSF establishes the very high speed Backbone
Network Service (vBNS) linking super-computing centers: NCAR, NCSA,
SDSC, CTC, PSC
- Neda Rayaneh Institute (NRI), Iran's first commercial provider, comes online,
connecting via satellite to Cadvision, a Canadian provider (:rm1:)
- Hong Kong police disconnect all but one of the colony's Internet providers
for failure to obtain a license; thousands of users are left without
service (:kf2:)
- Sun launches JAVA on May 23
- RealAudio, an audio streaming technology, lets the Net hear in near real-time
- Radio HK, the first commercial 24 hr., Internet-only radio station starts
broadcasting
- WWW surpasses ftp-data in March as the service with greatest traffic on NSFNet
based on packet count, and in April based on byte count
- Traditional online dial-up systems (CompuServe, America Online, Prodigy)
begin to provide Internet access
- Thousands in Minneapolis-St. Paul (USA) lose Net access after transients
start a bonfire under a bridge at the Univ of MN causing fiber-optic
cables to melt (30 July)
- A number of Net related companies go public, with Netscape leading the pack
with the 3rd largest ever NASDAQ IPO share value (9 August)
- Registration of domain names is no longer free. Beginning 14 September, a
$50 annual fee has been imposed, which up until now was subsidized by NSF.
NSF continues to pay for .edu registration, and on an interim basis for .gov
- The Vatican comes on-line (http://www.vatican.va/)
- The Canadian Government comes on-line (http://canada.gc.ca/)
- The first official Internet wiretap was successful in helping the Secret
Service and Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) apprehend three individuals who
were illegally manufacturing and selling cell phone cloning equipment
and electronic devices
- Operation Home Front connects, for the first time, soldiers in the field with
their families back home via the Internet.
- Richard White becomes the first person to be declared a munition, under
the USA's arms export control laws, because of an RSA file security
encryption program tattooed on his arm (:wired496:)
- RFC 1882: The 12-Days of Technology Before Christmas
- Country domains registered: Ethiopia (ET), Cote d'Ivoire (CI), Cook Islands (CK)
Cayman Islands (KY), Anguilla (AI), Gibraltar (GI), Vatican (VA),
Kiribati (KI), Kyrgyzstan (KG), Madagascar (MG), Mauritius (MU), Micronesia
(FM), Monaco (MC), Mongolia (MN), Nepal (NP), Nigeria (NG), Western Samoa
(WS), San Marino (SM), Tanzania (TZ), Tonga (TO), Uganda (UG), Vanuatu (VU)
- Top 10 Domains by Host #: com, edu, net, gov, mil, org, de, uk, ca, au
- Technologies of the Year: WWW, Search engines
- Emerging Technologies: Mobile code (JAVA, JAVAscript), Virtual environments
(VRML), Collaborative tools
- Hacks of the Year: The Spot (Jun 12), Hackers Movie Page (12 Aug)
- 1996
- Internet phones catch the attention of US telecommunication companies
who ask the US Congress to ban the technology (which has been around for years)
- Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad, PLO Leader Yasser Arafat, and
Phillipine President Fidel Ramos meet for ten minutes in an online
interactive chat session on 17 January.
- The controversial US Communications Decency Act (CDA) becomes law in the US
in order to prohibit distribution of indecent materials over the Net.
A few months later a three-judge panel imposes an injunction against
its enforcement. Supreme Court unanimously rules most of it
unconstitutional in 1997.
- 9,272 organizations find themselves unlisted after the InterNIC
drops their name service as a result of not having paid their domain name fee
- Various ISPs suffer extended service outages, bringing into question whether
they will be able to handle the growing number of users.
AOL (19 hours), Netcom (13 hours), AT&T WorldNet (28 hours - email only)
- Domain name tv.com sold to CNET for US$15,000
- New York's Public Access Networks Corp (PANIX) is shut down after repeated
SYN attacks by a cracker using methods outlined in a hacker magazine (2600)
- MCI upgrades Internet backbone adding ~13,000 ports, bringing the
effective speed from 155Mbps to 622Mbps.
- The Internet Ad Hoc Committee announces plans to add 7 new generic Top Level
Domains (gTLD): .firm, .store, .web, .arts, .rec, .info, .nom.
The IAHC plan also calls for a competing group of domain registrars worldwide.
- A malicious cancelbot is released on USENET wiping out more than 25,000 messages
- The WWW browser war, fought primarily between Netscape and Microsoft, has
rushed in a new age in software development, whereby new releases are
made quarterly with the help of Internet users eager to test upcoming
(beta) versions.
- RFC 1925: The Twelve Networking Truths
- Restrictions on Internet use around the world:
- China: requires users and ISPs to register with the police
- Germany: cuts off access to some newsgroups carried on CompuServe
- Saudi Arabia: confines Internet access to universities and hospitals
- Singapore: requires political and religious content providers to register
with the state
- New Zealand: classifies computer disks as "publications" that can be censored
and seized
- source: Human Rights Watch
- Country domains registered: Qatar (QA),
Central frican Republic (CF), Oman (OM), Norfolk Island (NF),
Tuvalu (TV), French Polynesia (PF), Syria (SY), Aruba (AW), Cambodia (KH),
French Guiana (GF), Eritrea (ER), Cape Verde (CV), Burundi (BI), Benin (BJ)
Bosnia-Herzegovina (BA), Andorra (AD), Guadeloupe (GP), Guernsey (GG),
Isle of Man (IM), Jersey (JE), Lao (LA), Maldives (MV), Marshall Islands (MH),
Mauritania (MR), Northern Mariana Islands (MP), Rwanda (RW), Togo (TG),
Yemen (YE), Zaire (ZR)
- Top 10 Domains by Host #: com, edu, net, uk, de, jp, us, mil, ca, au
- Hacks of the Year: US Dept of Justice (17 Aug), CIA (19 Sep), Air Force
(29 Dec), UK Labour Party (6 Dec), NASA DDCSOL - USAFE - US Air Force (30 Dec)
- Technologies of the Year: Search engines, JAVA, Internet Phone
- Emerging Technologies: Virtual environments (VRML), Collaborative
tools, Internet appliance (Network Computer)
- 1997
- 2000th RFC: "Internet Official Protocol Standards"
- 71,618 mailing lists registered at Liszt, a mailing list directory
- The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) is established to
handle administration and registration of IP numbers to the geographical
areas currently handled by Network Solutions (InterNIC), starting March 1998.
- CA*net II launched in June to provide Canada's next generation Internet
using ATM/SONET
- In protest of the DNS monopoly, AlterNIC's owner, Eugene Kashpureff,
hacks DNS so users going to www.internic.net end up at www.alternic.net
- Domain name business.com sold for US$150,000
- Early in the morning of 17 July, human error at Network Solutions causes the
DNS table for .com and .net domains to become corrupted, making millions of
systems unreachable.
- Longest hostname registered with InterNIC: CHALLENGER.MED.SYNAPSE.UAH.UALBERTA.CA
- 101,803 Name Servers in whois database
- RFC 2100: The Naming of Hosts
- Country domains registered: Falkland Islands (FK), East Timor (TP),
R of Congo (CG), Christmas Island (CX), Gambia (GM), Guinea-Bissau (GW),
Haiti (HT), Iraq (IQ), Libya (LY), Malawi (MW), Martinique (MQ),
Montserrat (MS), Myanmar (MM), French Reunion Island (RE), Seychelles (SC),
Sierra Leone (SL), Somalia (SO), Sudan (SD), Tajikistan (TJ), Turkmenistan (TM),
Turks and Caicos Islands (TC), British Virgin Islands (VG),
Heard and McDonald Islands (HM), French Southern Territories (TF),
British Indian Ocean Territory (IO), Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands (SJ),
St Pierre and Miquelon (PM), St Helena (SH), South Georgia/Sandwich Islands (GS),
Sao Tome and Principe (ST), Ascension Island (AC),
US Minor Outlying Islands (UM), Mayotte (YT), Wallis and Futuna Islands (WF),
Tokelau Islands (TK), Chad Republic (TD), Afghanistan (AF), Cocos Island (CC),
Bouvet Island (BV), Liberia (LR), American Samoa (AS), Niue (NU),
Equatorial New Guinea (GQ), Bhutan (BT), Pitcairn Island (PN), Palau (PW),
DR of Congo (CD)
- Top 10 Domains by Host #: com, edu, net, jp, uk, de, us, au, ca, mil
- Hacks of the Year: Indonesian Govt (19 Jan, 10 Feb, 24 Apr, 30 Jun, 22 Nov),
NASA (5 Mar), UK Conservative Party (27 Apr), Spice Girls (14 Nov)
- Technologies of the Year: Push, Multicasting
- Emerging Technologies: Push
- 1998
- Hobbes' Internet Timeline is released as RFC 2235 & FYI 32
- US Depart of Commerce (DoC) releases the Green Paper outlining
its plan to privatize DNS on 30 January. This is followed up by a
White Paper on June 5
- La Fête de l'Internet, a country-wide Internet fest,
is held in France 20-21 March
- Web size estimates range between 275 (Digital) and 320 (NEC) million pages for 1Q
- Companies flock to the Turkmenistan NIC in order to register their
name under the .tm domain, the English abbreviation for trademark
- Internet users get to be judges in a performance by 12 world champion ice skaters
on 27 March, marking the first time a television sport show's outcome is
determined by its viewers.
- Network Solutions registers its 2 millionth domain on 4 May
- Electronic postal stamps become a reality, with the US Postal Service allowing stamps
to be purchased and downloaded for printing from the Web.
- Canada kicks off CA*net 3, the first national optical internet
- Compaq pays US$3.3million for altavista.com
- CDA II and a ban on Net taxes are signed into US law (21 October)
- ABCNews.com accidentally posts test US election returns one day early
(2 November)
- Indian ISP market is deregulated in November causing a rush for ISP operation
licenses
- US DoC enters into an agreement with the Internet Corporation for Assigned
Numbers (ICANN) to establish a process for transitioning DNS
from US Government management to industry (25 November)
- San Francisco sites without off-city mirrors go offline as the
city blacks out on 8 December
- Chinese government puts Lin Hai on trial for "inciting the overthrow of
state power" for providing 30,000 email addresses to a US Internet magazine
(December) [ He is later sentenced to two years in jail ]
- French Internet users give up their access on 13 December to boycott France
Telecom's local phone charges (which are in addition to the ISP charge)
- Open source software comes of age
- RFC 2321: RITA -- The Reliable Internetwork Troubleshooting Agent
- RFC 2322: Management of IP numbers by peg-dhcp
- RFC 2323: IETF Identification and Security Guidelines
- RFC 2324: Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0)
- Country domains registered: Nauru (NR), Comoros (KM)
- Bandwidth Generators: Winter Olympics (Feb), World Cup (Jun-Jul),
Starr Report (11 Sep), Glenn space launch
- Top 10 Domains by Host #: com, net, edu, mil, jp, us, uk ,de, ca, au
- Hacks of the Year: US Dept of Commerce (20 Feb), New York Times (13 Sep),
China Society for Human Rights Studies (26 Oct), UNICEF (7 Jan)
- Technologies of the Year: E-Commerce, E-Auctions, Portals
- Emerging Technologies: E-Trade, XML, Intrusion Detection
- 1999
- Internet access becomes available to the Saudi Arabian (.sa) public in January
- vBNS sets up an OC48 link between CalREN South and North using Juniper
M40 routers
- First Internet Bank of Indiana, the first full-service bank available
only on the Net, opens for business on 22 February
- IBM becomes the first Corporate partner to be approved for Internet2 access
- European Parliament proposes banning the caching of Web pages by ISPs
- The Internet Fiesta kicks off in March across Europe, building on the success
of La Fête de l'Internet held in 1998
- US State Court rules that domain names are property that may be garnished
- MCI/Worldcom, the vBNS provider for NSF, begins upgrading the US backbone to
2.5GBps
- A forged Web page made to look like a Bloomberg financial news story
raised shares of a small technology company by 31% on 7 April.
- ICANN announces the five testbed registrars for the competitive Shared
Registry System on 21 April: AOL, CORE, France Telecom/Oléane,
Melbourne IT, Register.com. 29 additional post-testbed registrars are
also selected on 21 April, followed by 8 on 25 May, 15 on 6 July, and
so on for a total of 98 by year's end. The testbed, originally scheduled
to last until 24 June, is extended until 10 September, and then 30
November. The first registrar to come online is Register.com on 7 June
- First large-scale Cyberwar takes place simultaneously with the war in
Serbia/Kosovo
- Abilene, the Internet2 network, reaches across the Atlantic and connects
to NORDUnet and SURFnet
- The Web becomes the focal point of British politics as a list of MI6
agents is released on a UK Web site. Though forced to remove the list
from the site, it was too late as the list had already been replicated
across the Net. (15 May)
- Activists Net-wide target the world's financial centers on 18 June, timed
to coincide with the G8 Summit. Little actual impact is reported.
- MCI/Worldcom launches vBNS+, a commercialized version of vBNS
targeted at smaller educational and research institutions
- Somalia gets its first ISP - Olympic Computer (Sep)
- ISOC approves the formation of the Internet Societal Task Force (ISTF).
Vint Cerf serves as first chair
- Free computers are all the rage (as long as you sign a long term contract for
Net service)
- .ps is registered to Palestine (11 Oct)
- vBNS reaches 101 connections
- business.com is sold for US$7.5million (it was purchased in 1997 for
US$150,000 (30 Nov)
- RFC 2549: IP over Avian Carriers with Quality of Service
- RFC 2550: Y10K and Beyond
- RFC 2551: The Roman Standards Process -- Revision III
- RFC 2555: 30 Years of RFCs
- RFC 2626: The Internet and the Millennium Problem (Year 2000)
- Top 10 TLDs by Host #: com, net, edu, jp, uk, mil, us, de, ca, au
- Hacks of the Year: Star Wars (8 Jan), .tp (Jan), USIA (23 Jan),
E-Bay (13 Mar), US Senate (27 May), NSI (2 Jul), Paraguay Gov't
(20 Jul), AntiOnline (5 Aug), Microsoft (26 Oct), UK Railtrack (31 Dec)
- Technologies of the Year: E-Trade, Online Banking, MP3
- Emerging Technologies: Net-Cell Phones, Thin Computing, Embedded Computing
- Viruses of the Year: Melissa (March), ExploreZip (June)
- 2000
- The US timekeeper (USNO) and a few other
time services around the world report the new year as 19100 on 1 Jan
- A massive denial of service attack is launched against major web sites,
including Yahoo, Amazon, and eBay in early February
- Web size estimates by NEC-RI and Inktomi surpass 1 billion indexable pages
- ICANN redelegates the .pn domain, returning it to the Pitcairn Island
community (February)
- Internet2 backbone network deploys IPv6 (16 May)
- Various domain name hijackings took place in late May and early June, including
internet.com, bali.com, and web.net
- A testbed allowing the registration of domain names in Chinese, Japanese, and
Korean begins operation on 9 November. This testbed, created by VeriSign
without IETF authorization, only allows the second-level domain to be
non-English, still forcing use of .com, .net, .org.
The Chinese government blocks internal registrations, stating that
registrations in Chinese are its sovereignty right
- ICANN selects new TLDs: .aero, .biz, .coop, .info, .museum, .name, .pro (16 Nov)
- Mexico's connection to Internet2 becomes fully operational as the California
research network (CalREN-2) is connected with Mexico's Corporación
Universitaria para el Desarrollo de Internet (CUDI) network. Though connected
in November, the link's inauguration by California's Governor and Mexico's
President was not until March of 2001.
- After months of legal proceedings, the French court rules Yahoo! must block
French users from accessing hate memorabilia in its auction site (Nov).
Given its inability to provide such a block on the Internet, Yahoo! removes
those auctions entirely (Jan 2001).
- The European Commission contracts with a consortium of 30 national research
networks for the development of Géant, Europe's new gigabit research
network meant to enhance the current capability provided by TEN-155 (6 Nov)
- Australian government endorses the transfer of authority for the .au domain
to auDA (18 Dec). ICANN signs over control to auDA on 26 Oct 2001.
- RFC 2795: The Infinite Monkey Protocol Suite
- Hacks of the Year: RSA Security (Feb), Apache (May), Western Union (Sep),
Microsoft (Oct)
- Technologies of the Year: ASP, Napster
- Emerging Technologies: Wireless devices, IPv6
- Viruses of the Year: Love Letter (May)
- Lawsuits of the Year: Napster, DeCSS
- 2001
- The first live distributed musical -- The Technophobe & The Madman --
over Internet2 networks debuts on 20 Feb
- VeriSign extends its multilingual domain testbed to encompass various
European languages (26 Feb), and later the full Unicode character set (5 Apr)
opening up most of the world's languages
- Forwarding email in Australia becomes illegal with the passing of the Digital
Agenda Act, as it is seen as a technical infringement of personal copyright
(4 Mar)
- Radio stations broadcasting over the Web go silent over royalty disputes
(10 Apr)
- High schools in five states (Michigan, Missouri, Oregon, Virginia, and
Washington) become the first to gain Internet2 access
- US Dept of Commerce issues a notice of intent on 6 April to turn over
management for the .edu domain from VeriSign to Educase. Award
agreement is reached on 29 October. Community colleges
are finally be able to register under .edu
- Napster keeps finding itself embroiled in litigation and is eventually
forced to suspend service; it comes back later in the year as a
subscription service
- European Council finalizes an international cybercrime treaty on
22 June and adopts it on 9 November. This is the first treaty
addressing criminal offenses committed over the Internet.
- .biz and .info are added to the root server on 27 June with
registrations beginning in July. .biz domain go live on 7 Nov.
- Afghanistan's Taliban bans Internet access country-wide, including from
Government offices, in an attempt to control content (13 Jul)
- Code Red worm and Sircam virus infiltrate thousands of web servers and
email accounts, respectively, causing a spike in Internet bandwidth usage
and security breaches (July)
- A fire in a train tunnel running through Baltimore, Maryland seriously damages
various fiber-optic cable bundles used by backbone providers, disrupting
Internet traffic in the Mid-Atlantic states and creating a ripple effect
across the US (18 Jul)
- Brazil RNP2 is connected to Internet2's Abilene over 45Mbps line (21 Aug)
- GEANT, the pan-European Gigabit Research and Education Network, becomes
operational (23 Oct), replacing the TEN-155 network which was closed down (30 Nov)
- .museum begins resolving (Nov)
- First uncompressed real-time gigabit HDTV transmission across a wide-area
IP network takes place on Internet2 (12 Nov).
- Dutch SURFnet and Internet2's Abilene connect via gigabit ethernet (15 Nov)
- .us domain operational responsibility assumed by NeuStar (20 Nov)
- RFC 3091: Pi Digit Generation Protocol
- RFC 3092: Etymology of "Foo"
- RFC 3093: Firewall Enhancement Protocol (FEP)
- Viruses of the Year: Code Red (Jul), Nimda (Sep), SirCam (Jul), BadTrans (Apr, Nov)
- Emerging Technologies: Grid Computing, P2P
- 2002
- US ISP Association (USISPA) is created from the former CIX (11 Jan)
- .name begins resolving (15 Jan)
- .coop registrations begin (30 Jan)
- .aero registrations begin (18 Mar)
- RFC 3251: Electricity over IP
- RFC 3252: Binary Lexical Octet Ad-hoc Transport
If you enjoy the Timeline or make use of it in some way, please
consider a contribution.
Internet | Networks | WWW | USENET | Security
Internet growth:
Date Hosts | Date Hosts Networks Domains
----- --------- + ----- --------- -------- ---------
12/69 4 | 07/89 130,000 650 3,900
06/70 9 | 10/89 159,000 837
10/70 11 | 10/90 313,000 2,063 9,300
12/70 13 | 01/91 376,000 2,338
04/71 23 | 07/91 535,000 3,086 16,000
10/72 31 | 10/91 617,000 3,556 18,000
01/73 35 | 01/92 727,000 4,526
06/74 62 | 04/92 890,000 5,291 20,000
03/77 111 | 07/92 992,000 6,569 16,300
12/79 188 | 10/92 1,136,000 7,505 18,100
08/81 213 | 01/93 1,313,000 8,258 21,000
05/82 235 | 04/93 1,486,000 9,722 22,000
08/83 562 | 07/93 1,776,000 13,767 26,000
10/84 1,024 | 10/93 2,056,000 16,533 28,000
10/85 1,961 | 01/94 2,217,000 20,539 30,000
02/86 2,308 | 07/94 3,212,000 25,210 46,000
11/86 5,089 | 10/94 3,864,000 37,022 56,000
12/87 28,174 | 01/95 4,852,000 39,410 71,000
07/88 33,000 | 07/95 6,642,000 61,538 120,000
10/88 56,000 | 01/96 9,472,000 93,671 240,000
01/89 80,000 | 07/96 12,881,000 134,365 488,000
| 01/97 16,146,000 828,000
| 07/97 19,540,000 1,301,000
*** see Note below ***
Hosts = a computer system with registered ip address (an A record)
Networks = registered class A/B/C addresses
Domains = registered domain name (with name server record)
Note: A more accurate survey mechanism was developed in 1/98; new and
some corrected numbers are shown below. For further info, see
Sources section.
Date Hosts | Date Hosts | Date Hosts
----- ----------- + ----- ----------- + ----- -----------
01/95 5,846,000 | 01/97 21,819,000 | 01/99 43,230,000
07/95 8,200,000 | 07/97 26,053,000 | 07/99 56,218,000
01/96 14,352,000 | 01/98 29,670,000 | 01/00 72,398,092
07/96 16,729,000 | 07/98 36,739,000 | 07/00 93,047,785
| 01/01 109,574,429
| 07/01 125,888,197
| 01/02 147,344,723
| 07/02 162,128,493
Figure: Internet Hosts
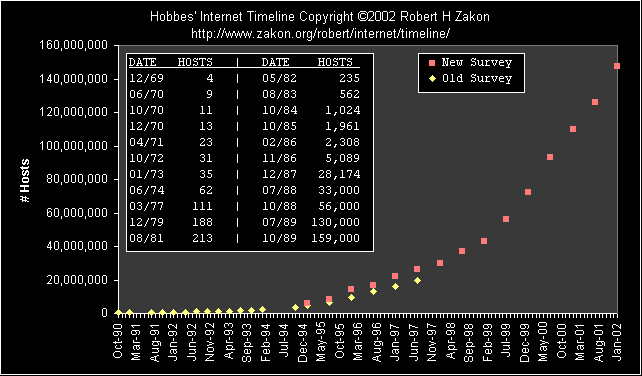
click here for a chart showing the logarithmic growth of the Internet
Figure: Internet Domains

Figure: Internet Networks
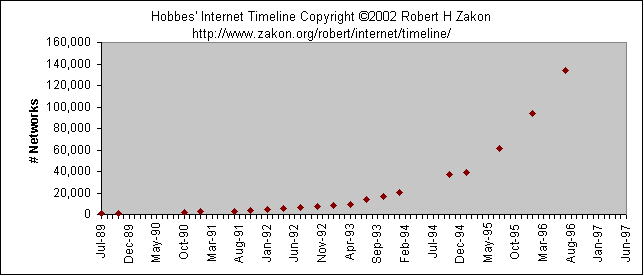
Worldwide Networks Growth: (I)nternet (B)ITNET (U)UCP (F)IDONET (O)SI
____# Countries____ ____# Countries____
Date I B U F O Date I B U F O
----- --- --- --- --- --- ----- --- --- --- --- ---
09/91 31 47 79 49 02/94 62 51 125 88 31
12/91 33 46 78 53 07/94 75 52 129 89 31
02/92 38 46 92 63 11/94 81 51 133 95 --
04/92 40 47 90 66 25 02/95 86 48 141 98 --
08/92 49 46 89 67 26 06/95 96 47 144 99 --
01/93 50 50 101 72 31 06/96 134 -- 146 108 --
04/93 56 51 107 79 31 07/97 171 -- 147 108 --
08/93 59 51 117 84 31
Figure: Worldwide Networks Growth

WWW Growth:
Date Sites | Date Sites | Date Sites
----- ---------- + ----- ---------- + ----- ----------
06/93 130 | 09/97 1,364,714 | 11/99 8,844,573
09/93 204 | 10/97 1,466,906 | 12/99 9,560,866
10/93 228 | 11/97 1,553,998 | 01/00 9,950,491
12/93 623 | 12/97 1,681,868 | 02/00 11,161,811
06/94 2,738 | 01/98 1,834,710 | 03/00 13,106,190
12/94 10,022 | 02/98 1,920,933 | 04/00 14,322,950
06/95 23,500 | 03/98 2,084,473 | 05/00 15,049,382
01/96 100,000 | 04/98 2,215,195 | 06/00 17,119,262
03/96 135,396 | 05/98 2,308,502 | 07/00 18,169,498
04/96 150,295 | 06/98 2,410,067 | 08/00 19,823,296
05/96 193,150 | 07/98 2,594,622 | 09/00 21,166,912
06/96 252,000 | 08/98 2,807,588 | 10/00 22,282,727
07/96 299,403 | 09/98 3,156,324 | 11/00 23,777,446
08/96 342,081 | 10/98 3,358,969 | 12/00 25,675,581
09/96 397,281 | 11/98 3,518,158 | 01/01 27,585,719
10/96 462,047 | 12/98 3,689,227 | 02/01 28,125,284
11/96 525,906 | 01/99 4,062,280 | 03/01 28,611,177
12/96 603,367 | 02/99 4,301,512 | 04/01 28,669,939
01/97 646,162 | 03/99 4,349,131 | 05/01 29,031,745
02/97 739,688 | 04/99 5,040,663 | 06/01 29,302,656
03/97 883,149 | 05/99 5,414,325 | 07/01 31,299,592
04/97 1,002,612 | 06/99 6,177,453 | 08/01 30,775,624
05/97 1,044,163 | 07/99 6,598,697 | 09/01 32,398,046
06/97 1,117,259 | 08/99 7,078,194 | 10/01 33,135,768
07/97 1,203,096 | 09/99 7,370,929 | 11/01 36,458,394
08/97 1,269,800 | 10/99 8,115,828 | 12/01 36,276,252
| 01/02 36,689,008
| 02/02 38,444,856
| 03/02 38,118,962
Sites = # of web servers (one host may have multiple sites by
using different domains or port numbers)
Figure: WWW Growth
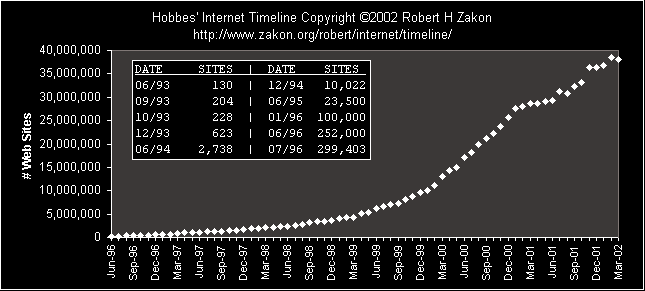
click here for a chart showing the logarithmic growth of the Web
USENET Growth:
Date Sites ~MB ~Posts Groups | Date Sites ~MB ~Posts Groups
---- ----- --- ------ ------ + ---- ------- --- ------ ------
1979 3 2 3 | 1987 5,200 2 957 259
1980 15 10 | 1988 7,800 4 1933 381
1981 150 0.05 20 | 1990 33,000 10 4,500 1,300
1982 400 35 | 1991 40,000 25 10,000 1,851
1983 600 120 | 1992 63,000 42 17,556 4,302
1984 900 225 | 1993 110,000 70 32,325 8,279
1985 1,300 1.0 375 | 1994 180,000 157 72,755 10,696
1986 2,200 2.0 946 241 | 1995 330,000 586 131,614
~ approximate: MB - megabytes per day, Posts - articles per day
Security (CERT) Incidents:
Date Incidents Advisories Vulnerabilities
---- --------- ---------- ---------------
1988 6 1
1989 132 7
1990 252 12
1991 406 23
1992 773 21
1993 1,334 19
1994 2,340 15
1995 2,412 18 171
1996 2,573 27 345
1997 2,134 28 311
1998 3,734 13 262
1999 9,859 17 417
2000 21,756 22 774
2001 52,658 37 2,437
- 1. How do I get Hobbes' Internet Timeline?
- The Timeline is archived at http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/.
Should you only have email access, you can learn how to request this
document and access the rest of the Internet by sending an email to one of
the following addresses.
- mail-server@rtfm.mit.edu (Americas) with the following line in the
body of the message:
send usenet/news.answers/internet-services/access-via-email
- mailbase@mailbase.ac.uk (elsewhere) with the following line in the body
of the message:
send lis-iis e-access-inet.txt
- 2. Is the Timeline available in other languages or editions?
-
If you are interested in translating to another language or format, email me first
- 3. Can I re-print the Timeline or use parts of it for ... ?
- Drop me an email. The answer is most likely (though don't assume) 'yes'
for non-profit use, and 'maybe' for for-profit; but to be sure you are not
going to break any copyright laws, drop me an email and wait for a reply.
Also, please note that I get a bunch of requests with improperly formatted
return email addresses. If you don't hear from me in a week (typical turn
around is < 1 hour), check your header and email again. BTW, don't
forget to tell me who you are and your affiliation; anonymous requests
will not be answered.
- 4. What do you do when not updating the Timeline?
- For fun: travel, photography, R/C boats, developing technology prototypes
ranging from robots, speech to speech translators, and an assortment of
Web capabilities. Professionally: evangelize/research/develop
advanced Internet, Web, e-commerce and multilingual computing technologies.
Explore www.Zakon.org to learn more.
- 0. Peddie (Ala Viva!), CWRU (North Side), Amici usque ad aras (PHP OH-EP),
Colégio Andrews (Rio), Gordonstoun (Elgin)
- E-mail me if you know
Hobbes' Internet Timeline was compiled from a number of sources, with some
of the stand-outs being:
Cerf, Vinton (as told to Bernard Aboba). "How the Internet Came to Be."
This article appears in "The Online User's Encyclopedia," by Bernard Aboba.
Addison-Wesley, 1993.
Hardy, Henry. "The History of the Net." Master's Thesis, School of
Communications, Grand Valley State University.
http://www.ocean.ic.net/ftp/doc/nethist.html
Hardy, Ian. "The Evolution of ARPANET email." History Thesis, UC Berkeley.
http://www.ifla.org/documents/internet/hari1.txt
Hauben, Ronda and Michael. "The Netizens and the Wonderful World of the Net."
http://www.columbia.edu/~hauben/netbook/
Kulikowski, Stan II. "A Timeline of Network History." (author's email below)
Quarterman, John. "The Matrix: Computer Networks and Conferencing Systems
Worldwide." Bedford, MA: Digital Press. 1990
"ARPANET, the Defense Data Network, and Internet". Encyclopedia of
Communications, Volume 1. Editors: Fritz Froehlich, Allen Kent.
New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 1991
Internet growth summary compiled from:
- Zone program reports maintained by Mark Lottor at:
ftp://ftp.nw.com/pub/zone/
Note: A more accurate host counting mechanism was used starting
with 1/98 count.
- Connectivity table maintained by Larry Landweber at:
ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/connectivity_table/
- ARPAnet maps published in various sources
WWW growth summary compiled from:
- Web growth summary page by Matthew Gray of MIT:
http://www.mit.edu/people/mkgray/net/web-growth-summary.html
- Netcraft at http://www.netcraft.com/survey/
USENET growth summary compiled from Quarterman and Hauben sources above,
and news.lists postings. Lots of historical USENET postings also provided
by Tom Fitzgerald (fitz@wang.com).
CERT growth summary compiled from CERT reports at ftp://ftp.cert.org/
CERT stats are also now being made available by CERT at
http://www.cert.org/stats/cert_stats.html
Many of the URLs provided by Arnaud Dufour (arnaud.dufour@hec.unil.ch)
Country-specific Internet Histories:
- Australia - "A Brief History of the Internet in Australia" by Roger Clarke
http://www.anu.edu.au/people/Roger.Clarke/II/OzIHist.html
- Australia - "It Started with a Ping" by Jennie Sinclair
http://www.aarnet.edu.au/corporate/history/sinclair.html
- Brazil - "Linha to Tempo da Internet no Brasil" by Érico Guizzo
http://www.lsi.usp.br/~emguizzo/inetbr/
- UK - "Early Experiences with the ARPANET and INTERNET in the UK" by Peter Kirstein
http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/jon/arpa/internet-history.html
Additional books of interest:
- "Weaving the Web : The Original Design and Ultimate Destiny of the World Wide Web
by its Inventor"
by Tim Berners-Lee
- "Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins of the Internet"
by Katie Hafner & Matthew Lyon
- "Nerds 2.0.1: A Brief History of the Internet"
by Stephen Segaller
- "Architects of the Web: 1,000 Days That Built the Future of Business"
by Robert H. Reid
- "Netizens: On the History and Impact of Usenet and the Internet"
by Michael Hauben et al
- "Exploring the Internet: A Technical Travelogue"
by Carl Malamud
Early works of interest:
- "As We May Think" by Vannevar Bush, 1945
http://www.theatlantic.com/unbound/flashbks/computer/bushf.htm
- "Man-Computer Symbiosis" by J.C.R. Licklider, 1960
http://gatekeeper.dec.com/pub/DEC/SRC/research-reports/abstracts/src-rr-061.html
---
Contributors to Hobbes' Internet Timeline have their initials next to the
contributed items in the form (:zzz:) and are:
ad1 - Arnaud Dufour (arnaud.dufour@hec.unil.ch)
amk - Alex McKenzie (mckenzie@bbn.com)
bb1 - Billy Brackenridge (billyb@microsoft.com)
clg - C. Lee Giles (giles@research.nj.nec.com)
dk1 - Daniel Karrenberg (Daniel.Karrenberg@ripe.net)
ec1 - Eric Carroll (eric@enfm.utcc.utoronto.ca)
esr - Eric S. Raymond (esr@locke.ccil.org)
feg - Farrell E. Gerbode (farrell@is.rice.edu)
gb1 - Gordon Bell (GBell@microsoft.com)
gck - Gary C. Kessler (kumquat@hill.com)
glg - Gail L. Grant (grant@glgc.com)
gmc - Grant McCall (g.mccall@unsw.edu.au)
gst - Graham Thomas (G.S.Thomas@uel.ac.uk)
irh - Ian R Hardy (hardy@uclink2.berkeley.edu)
jap - Jean Armour Polly (mom@netmom.com)
jg1 - Jim Gaynor (gaynor@niherlas.com)
kf1 - Ken Fockler (fockler@hq.canet.ca)
kf2 - Kinming Fung (kinming@cuhk.edu.hk)
lb1 - Larry Backman (backman@ultranet.com)
lhl - Larry H. Landweber (lhl@cs.wisc.edu)
mpc - Mellisa P. Chase (pc@mitre.org)
pb1 - Paul Burchard (burchard@cs.princeton.edu)
pds - Peter da Silva (peter@baileynm.com)
ph1 - Peter Hoffman (hoffman@ece.nps.navy.mil)
rab - Roger A. Bielefeld (rab@hal.cwru.edu)
rm1 - Rahi Moosavi (r.moosavi@asrecomputer.com)
sc1 - Susan Calcari (susanc@is.internic.net)
sk2 - Stan Kulikowski (stankuli@uwf.bitnet) - see sources section
sw1 - Stephen Wolff (swolff@cisco.com)
tb1 - Tim Burress (tim@twics.com)
tp1 - Tim Pozar (pozar@kumr.lns.com)
vgc - Vinton Cerf (vcerf@isoc.org) - see sources section
wz1 - W. Zorn (zorn@ira.uka.de)
zby - Zenel Batagelj (zenel.batagelj@uni-lj.si)
:-) :-) :-) :-) :-) :-) ;-) Help the Author (-: (-: (-: (-: (-: (-: (-:
Thank you to the thousands of Net folks who contributed information to help
the author's genealogical search, yielding 45 new Zakon's from around the world!
Archive-name: Hobbes' Internet Timeline
Version: 5.6
Archive-location: http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/
Last-updated: 1 April 2002
Maintainer: Robert H'obbes' Zakon, Robert@Zakon.org, www.Zakon.org
Description:
An Internet timeline highlighting some of the key events and technologies
which helped shape the Internet as we know it today.







